How Secure is that Third Party Mobile App?

In a world where business is increasingly conducted on mobile devices, it is imperative that organizations offer mobile applications to serve their customer base. In fact, for many businesses, mobile applications are one of the primary channels used to interact with customers and to sell products and services.
Developing a secure mobile application can be challenging. Significant security risks are introduced when these applications are not continuously monitored for new vulnerabilities and potential threats. Take, for example, the recent Under Armour “My Fitness Pal” application breach. The security incident caused serious damage; in addition to impacting roughly 150 million users, public shares fell nearly 5% just days after the breach was announced.
As mobile applications continue to pose looming threats, Bitsight researchers leveraged data from their mobile application security risk vector to identify if mobile applications offered on iOS and Google Play stores have known security vulnerabilities and issues.
Our Methodology
Bitsight examined representative samples of more than 1,000 companies in each of the following industry sectors that offer mobile applications on iOS and Google Play:
- Business Services: Consumer Services, Human Resources, Management Consulting, Marketing and Advertising, Logistics and Supply Chain companies.
- Finance: Banking, Investment Management, Venture Capital, and Private Equity companies.
- Technology: Software, Networking, Security, Medical Devices, and Semiconductor companies.
- Education: Higher Education, Primary/Secondary Education, E-Learning, and Education Management companies.
- Media/Entertainment: Music, News, Media, Publishing, and Entertainment companies.
Mobile applications were tested for known security vulnerabilities and issues that are documented in The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), a free and open industry standard for assessing security vulnerabilities.
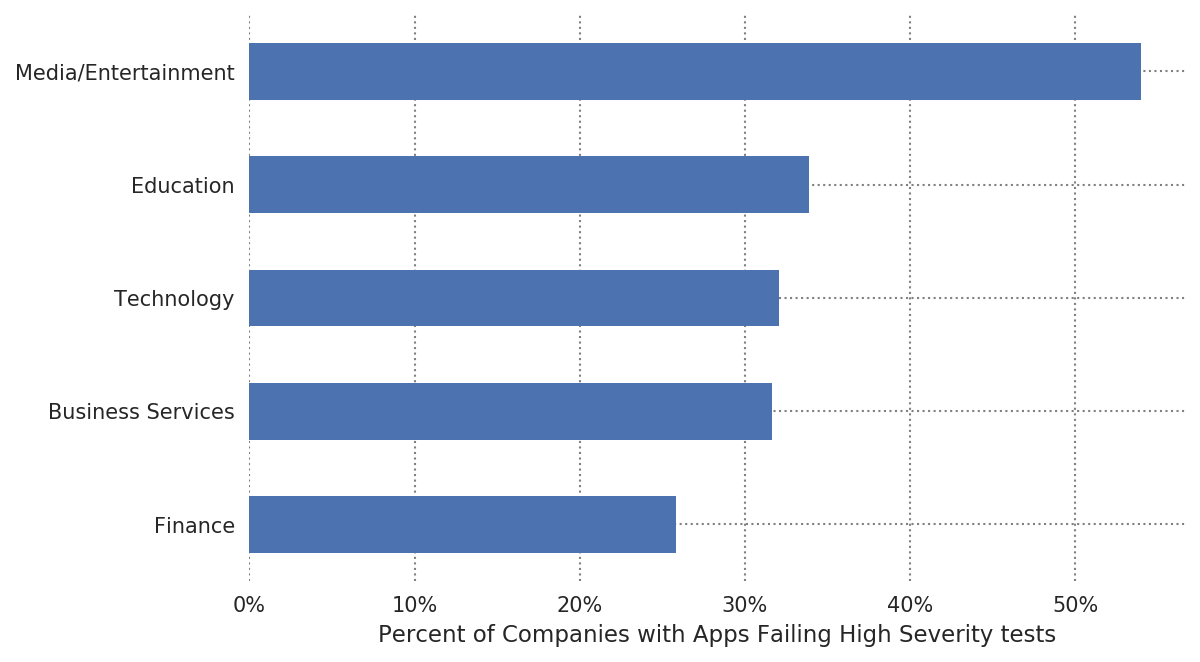
Based on the data, Bitsight uncovered industries that are most often faced with mobile application security challenges. We looked at the rate of companies in each industry that offer at least one mobile application that did not pass a high severity test: a CVSS score of 7 and above qualifies as high severity.
What We Learned
The results show that many industries are offering a significant percentage of mobile applications that have high severity vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities include (but are not limited to): data leakage, privilege abuse, unencrypted personally identifiable information (PII), and credential theft.
At a High Level:
- Over half of the companies studied in the Media/Entertainment industry offer risky mobile applications.
- One in four Finance companies offer risky mobile applications, which may pose greater risk of bank accounts being accessed without proper authorization or the exposure of payment information.
- In Education, with many universities offering numerous applications, these could present a considerable risk to the data of students and prospective students, as well as faculty.
The Most Common Vulnerabilities By Industry
For applications that did fail high severity tests, which vulnerabilities were most common? Bitsight looked at data from roughly 10,000 applications using its mobile application security risk vector data and observed which vulnerabilities were most common in each industry.
The Finance industry had the highest rate of broken SSL configurations (invalid TLS/SSL certificates): over 34% of applications that failed high severity tests in the Finance industry could be vulnerable to man-in-the-middle (MITM) and other attacks that can compromise data. Over 32% of Business Services and Education mobile applications that failed high severity tests are not encrypting end-user data, such as the IP address of devices using the application.
Finally, over 10% of Media/Entertainment and Education applications that failed high severity tests have unencrypted location data, meaning attackers may be able to glean location and GPS data on end-users. Combined with stolen credentials, or any data that is personally identifiable, this presents a large risk of sophisticated social engineering attacks on an application’s user base. 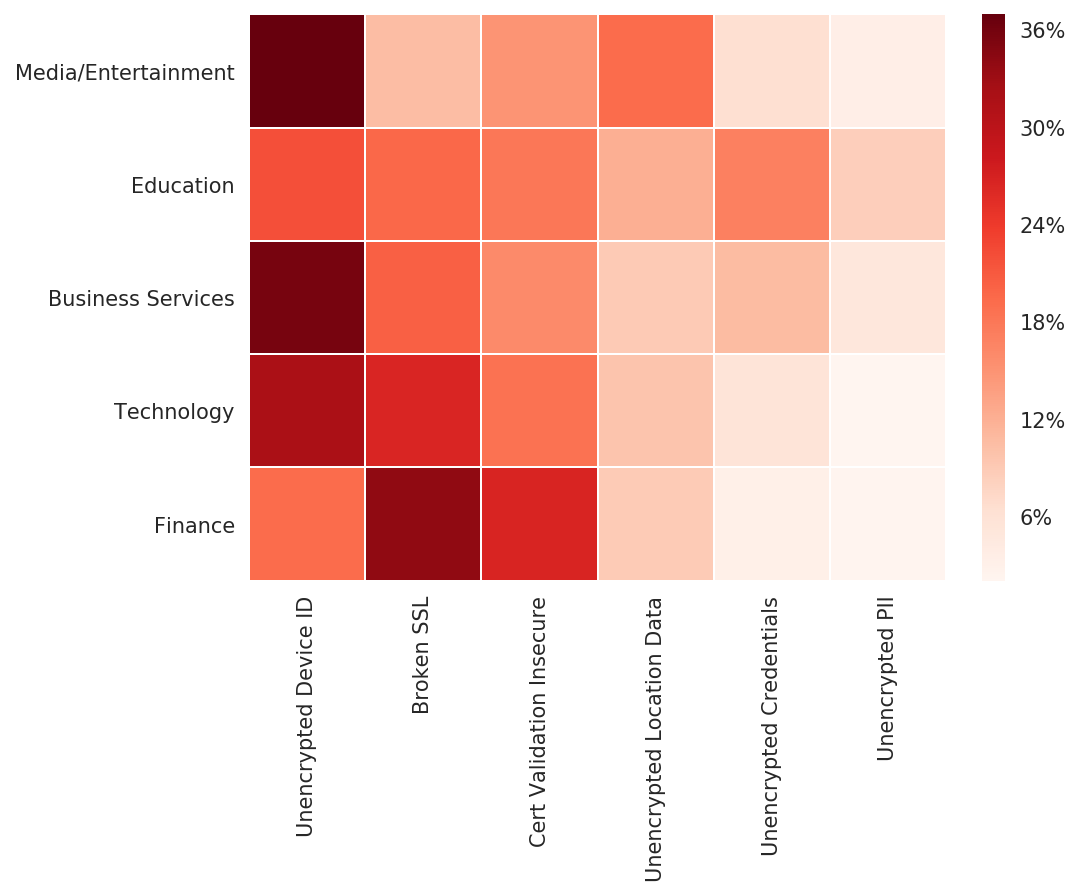
Key Takeaways:
As our analysis confirms, companies are struggling to secure their iOS and Android-based mobile applications. Bitsight works with customers to understand which third party business partners and vendors offer apps predisposed to security vulnerabilities. This holistic view into a company’s vendor ecosystem will not only identify potential threats, but it can also paint a bigger picture on the current processes and controls in need of a security makeover.