Content Security Policy Limits Dangerous Activity… So Why Isn’t Everyone Doing It?
Tags:

Online services, e-commerce sites, videoconference, delivery services, and all other kinds of services are growing exponentially, exposing users and data to new risks and threats. Users expect that the sites and services they rely on are using best practices when it comes to security. But are they?
To better understand web application security posture, Bitsight researchers examined the usage of Content Security Policy (CSP) across the global Internet since 2017. CSP is a W3C recommended security standard that “defines a mechanism by which web developers can control the resources which a particular page can fetch or execute, as well as a number of security-relevant policy decisions.” The technology is about 10 years old, and had 3 versions over this time. All major Internet browsers implement CSP.
CSP is designed to prevent cross-site scripting (XSS), clickjacking, “Man in the Middle” attacks, and other code injection attacks. XSS has become a common attack vector for malicious actors to target web applications and their private data. The threat and dangers of XSS include stealing credentials, sessions, or delivering malware to the victim. In recent months, attackers operating under the “Magecart” group have utilized hacking techniques like to inject malicious code into websites to steal data. Organizations like British Airways who failed to implement basic steps to reduce risk from these attacks have faced significant fines for their failures.
With new risks in play, Bitsight researchers wanted to evaluate whether organizations are actually implementing CSP and how that has changed over time. In summary, Bitsight researchers found:
- The adoption of CSP has increased significantly since 2017
- There is broad, consistent adoption of CSP across all sectors
- Larger organizations are more likely to use CSP
- The rate of usage of CSP is highest with the Top 1000 most visited websites, although the rate of adoption even by these website is only 24.5%
- Even though CSP adoption has increased, only 2% of sites have implemented “perfect” CSP; the vast majority of CSP adoption is missing key data or involves unsafe adoption
- Bitsight customers adopt CSP at a higher rate than the global Internet
Bitsight is able to assess CSP implementation by continuously monitoring global web application security issues. We can assess over time, at Internet-wide scale, the implementation and evolution of adoption of technologies dedicated to offer better security to web applications -- including CSP.
About the Study
Bitsight researchers studied the evolution of CSP from 2017 until the end of May 2020. The study includes 9 billion successful HTTP responses observed, making an average of 7 million observations a day. Of these observations one third were obtained from web applications using TLS/SSL.
This study includes overall usage of CSP and how we see it across different dimensions.
- Overall presence ratio over time
- By industry sector
- By organization size
- By common subdomain
- If present on network devices as Routers, Media Servers, NAS, PBX, IP Phones or Cameras, SSL VPNs, Printers
- If belonging to the most famous and used websites
- Bitsight customers versus Rest of the World
Overall presence ratio over time
Since 2017, there has been an increase in HTTP daily responses that include the Content Security Policy header or HTML meta tag. In 2017, only 1.5% of records were observed to have the CSP header; this is now 6.3%.

If we aggregate this data by month, we see that almost 5 million web applications use CSP now. These web applications either are from corporate websites or from network devices.

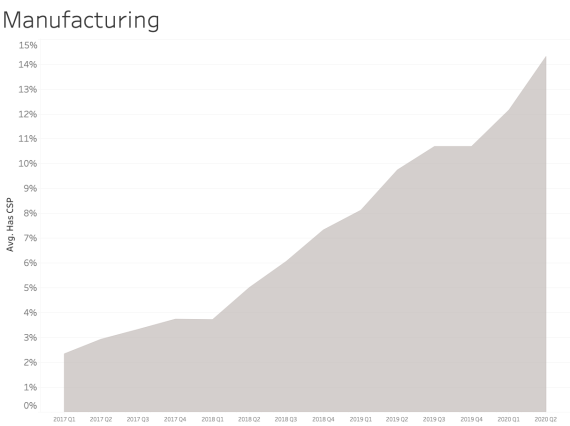
CSP presence by Industry Sector
In examining CSP presence by industry sector, most sectors appear to adopt CSP at a similar rate over time. We see consistent and steady adoption rates of CSP across all of the sectors that Bitsight tracks.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
By organization size
The study suggests that the larger an organization is, the more likely is to use CSP on web applications.

At common subdomains where security is paramount. (ex: www., service., shop., store., mail., webmail., remote., vpn., ftp., blog., forum., admin. )
When seen at common subdomains we see only a small increase in the ratio of usage.

However, shop., vpn. and blog. have a bigger presence than other names.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
With these results, we took special attention to the VPN services, and we detected several major vendors releasing new versions of their devices or operating systems including the CSP on web applications.
Mainstream and top ranking websites
The Internet wide survey CSP can’t be done without looking at the part of the Internet that common people and companies use daily. Bitsight researchers looked at the most famous and used websites and services in the World to examine the prevalence of CSP usage on those websites.
We divided websites on 3 slots based on a top usage ranking:
- 1000 (thousand)
- 10000 (ten thousand)
- 100000 (one hundred thousand)

Some of the best known domains and leaders on e-commerce, paying services, social media have a large ratio of CSP presence. We also observed that some of the companies that saw a large influx of global usage during the pandemic have responded to implement CSP.
However, the deployment of this technology can’t yet be seen as the rule or a common best practice followed by the top sites.
Completeness of CSP Policies
On the technical side, we also checked how well constructed and safe are all CSP policies published by web applications. From the published Content Security Policy, only 2% can be considered totally safe and perfect.

The reasons behind some of imperfect CSP policies are mainly the usage of unsafe inline and eval scripts.

Bitsight Customer Adoption of CSP Compared to Global Internet
Finally, Bitsight examined our Customers and tried to understand how they are adopting the Content Security Policy and compared the adoption rate to broader Internet adoption. We found that Bitsight customers are adopting CSP at rates that are significantly higher than the global Internet.

In Conclusion
Though the adoption of CSP has increased over the last 3 years, there is clearly more work that must be done. Attackers continue to exploit vulnerabilities that could be mitigated by deploying CSP. While larger organizations and a number of the most popular websites are adopting CSP, gaps still exist in broader adoption rates. Bitsight is proud that our customers are adopting CSP at a rate higher than the global Internet. However, more organizations will need to adopt CSP in order to reduce the risk that customer data is exposed to attackers. Additional work is required to explore legal and policy recommendations that would improve the adoption rate of CSP.


